In today’s data-driven world, compelling visual storytelling is not just an added value— it’s a necessity. The challenge many organizations face, however, is ensuring their data visualizations don’t just captivate audiences—they also remain accessible and meaningful for all users, including those with disabilities. Embracing accessibility in your visual reporting isn’t merely compliance-focused.
It’s a strategic approach that empowers your insights, boosts engagement, and amplifies your analytics efforts. Whether your data is internal and serving decision-makers or external-facing to stakeholders or the general public, accessible data visualizations support informed, inclusive decision-making. Let’s unravel the essentials of crafting data-driven visuals and explore actionable strategies to strengthen your organization’s initiatives in creating accessible, inclusive visual experiences.
Understanding Accessibility in the Context of Data Visualization
Accessibility, in the simplest terms, involves ensuring user interfaces—including data visualizations—are understandable and navigable by everyone. This includes users with visual impairments, color blindness, cognitive differences, and motor skill limitations. Accessible visualizations thoughtfully include all these variable user needs right from the design phase.
In the world of analytics, accessibility goes beyond simply adhering to compliance guidelines. It’s about empowering your organization and maximizing the reach and potential impact of your data insights. A stakeholder reliant on a screen reader should have access equal to their visually-able colleague when it comes to comprehending the relevance and significance of important business metrics. Accessibility also improves the overall user experience for all users, often leading to cleaner, simpler, and easily comprehensible designs.
It’s crucial for your team to recognize the business and ethical advantages of building accessibility directly into your analytics workflow. Accessibility considerations enhance trust, transparency, and stakeholder confidence. Companies investing strategically in accessible visualizations also inherently build stronger relationships internally and externally—fostering more inclusive workplace cultures, broader customer bases, and driving innovation forward through empathy and thoughtful inclusion.
Key Principles for Creating Accessible Data Visualizations
Prioritize Color and Contrast for Comprehensive Clarity
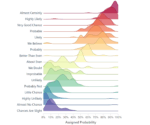
Effective color usage and contrast are integral in making visualizations accessible. Colors should be distinguishable by users who have various forms of color blindness. To achieve this, consider using highly contrasting colors and leveraging tools that simulate color-blindness views to test your visualizations. This small step ensures stakeholders do not miss important insights hidden behind inaccessible color schemes.
Beyond just selecting accessible colors, it’s essential to avoid relying exclusively on colors to communicate critical information. Consider pairing color with textures and patterns to provide additional visual signals. Clearly defined visual boundaries and consistently prominent labeling also aid clarity profoundly, empowering all users to derive deeper and quicker insights from visualizations.
Ensure Interactive Features and Navigation Are Keyboard-Optimized
Many visualization platforms offer interactive features like hover states or filters that may conventionally require the use of a mouse. However, accessibility demands keyboard navigation options, as some users may face challenges using a traditional mouse. To guarantee your visual analytics are inclusive, incorporate simple guidelines around tab stops, keyboard shortcuts, and ensure logical tab order.
A robust keyboard-friendly design includes not only navigational capabilities but also accessible tooltips and explicit instructional text that help every user quickly perceive how to engage with interactive features. Thoughtful attention here enhances usability significantly while aligning your organization with industry-leading accessibility best practices.
Provide Alternative Text and Contextual Descriptions
Even the most compelling visualizations become inaccessible to visually impaired users without appropriate alternative text. Alternative (“alt”) text assists users leveraging screen readers and other assistive technology to comprehend the important message a visualization intends to deliver.
An effective meaningful alt text should precisely and succinctly describe the visualization type and the key insights it communicates—especially significant trends, notable outliers, or strategic data points. Complementary long-form contextual descriptions accompanying highly complex graphics help provide deeper context, facilitating meaningful understanding regardless of varying user abilities. Incorporating thorough alt descriptions conveys transparency in analytics and ensures critical data stories resonate clearly across every group of stakeholders.
Putting Accessibility into Practice with Strategic Approaches
Layering Semantic Context into Your Analytics Workflow
An effective way to provide clear and consistent accessible visualizations starts with a solid semantic framework. A comprehensive semantic layer in analytics organizes your data terminology and structures clearly and consistently. Semantic layers provide a foundation for richer, consistent context within visualizations, ensuring data alignment across stakeholders— meaningful for usability and particularly beneficial for assistive technologies.
Strategically embedding a semantic layer within your data visualization design simplifies the interpretation experience for everyone involved. With clear dimensions, measures, named conventions and descriptions established through a semantic layer, users across all abilities find it easier to navigate, comprehend, and make more informed data-driven decisions.
Incorporating Accessibility Early with Collaborative Working Sessions
To effectively embed accessibility, engage diverse teams early. Launch your visualization efforts with collaborative working sessions involving stakeholders across various disciplines. Implementing analytics-focused working sessions early and often can significantly enhance clarity, reduce miscommunications, and collectively build visualization standards that cater inclusively to user needs.
Utilizing structured working sessions provides your analytics team a systematic approach to understanding end-users deeply, their individual challenges, and expectations around key data visualizations. By embedding accessibility early into visualization workflows, potential design obstacles are proactively circumvented, optimized visualization standards are established, and your analytics delivery becomes a transformational tool in creating inclusive insights.
Leverage Technology and Expertise to Improve Visualization Accessibility
Employing robust technologies and expert guidance significantly elevates your organization’s capabilities in accessible visualization creation. Consider partnering with professionals specializing in data visualization consulting services to help you architect solutions tailored specifically to meet accessibility best practices and enhance innovation within analytics.
Additionally, exploring relevant technological insights like understanding efficient execution of single-processor and asynchronous environments—as discussed in this informative breakdown on Node.js asynchronous processing—helps transition theoretical accessibility principles into practical reality. Expert knowledge and purposeful technology usage enhance overall visualization strategies, creating achievable paths toward comprehensive accessibility and long-term sustainability.
Conclusion: Building an Inclusive Data Culture
Creating accessible data visualizations is far more than just a mere checkmark for compliance—it’s a careful consideration of your audience’s diverse needs, and strategically empowering your analytics narrative. By thoughtfully embedding layouts, semantic clarity, keyboard-friendly navigations, and robust alt texts in your analytics framework, innovation within your organization accelerates naturally.
Your journey towards accessibility will thrive with purposeful training, strategic collaboration, practical technology application, and professional thinking. Adopting these best practices transforms your organization’s perception of analytics: from inclusive design into second-nature, driving continuous improvement, enhanced analytics adoption, and more impactful data-driven storytelling across every function in your business.
Accessibility strengthens analytics initiatives from mere reporting into influential, universally insightful storytelling—cultivating innovation, trust, and sustainable engagement through inclusive data visualizations for all.