by tyler garrett | May 24, 2025 | Data Processing
Data evolves—a reality that modern enterprises understand only too well. As businesses strive to draw accurate insights from increasingly vast and dynamic data sets, effectively managing these changes becomes critical. Among the crucial challenges data teams face when developing robust analytics solutions or designing sophisticated data warehouses is the implementation of Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCDs). Addressing how dimensions—attributes of business relevance like products, customers, or internal resources—change over time is fundamental to enhancing analytical accuracy and reliability. But what exactly does this entail, and how can your organization seamlessly integrate Slowly Changing Dimensions into your modern data platforms? In this guide, we’ll unravel the strategic importance of these dimensions, explore standard SCD methodologies, and dive deep into best practices and innovations transforming how businesses maintain historical accuracy while enabling powerful analytics and decision-making capabilities.
Understanding Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCD)
To grasp the power and importance of Slowly Changing Dimensions, we first need clarity around the concept itself. A dimension, in the realm of data warehousing and analytics, signifies descriptive attributes of business entities—such as geographic location, pricing tiers, employee roles, or customer profiles—that typically provide context to numerical facts. Over time, some of these descriptive attributes can incrementally shift, altering how businesses analyze or compare datasets historically versus in real-time. This slow evolution poses unique complexities in accurately tracking and representing changes within your analytics framework. Employing established strategies to manage Slowly Changing Dimensions effectively addresses the inherently temporal nature of analytics data, enabling accurate historical reporting and future forecasting.
Moreover, thoughtful attention to Slowly Changing Dimensions enhances decision-making clarity and minimizes distortion in analysis outcomes. Consider a company adapting pricing structures, reorganizing a sales territory, or altering customer loyalty classifications—tracking these changes accurately ensures stakeholders can see valid comparisons, trends, and performance improvements over any given timeframe. Ensuring historical accuracy isn’t just an ideal, it’s critical for enterprises looking to achieve clear visibility into performance analytics, strategic planning, and precise decision-making. Businesses mature enough to leverage these historical insights constantly drive considerable growth using data analytics insights.
Exploring Types of SCD Approaches
Type 1: Overwriting Data (Lose Historical Data)
The most straightforward approach, known as Type 1 Slowly Changing Dimensions, involves directly overwriting existing attribute values when a change occurs, maintaining no prior historical state. While simple and easy to implement in most databases or solutions like MySQL, the significant limitation arises when historical insights become critical. Type 1 SCD is commonly used when historical accuracy has minimal relevance, typically when correcting data errors or updating minor fields irrelevant to analytical trend analyses.
However, while simpler, its ramifications regarding historical analytics can be profound. If a critical dimension—like customer region—is overwritten without traceability, historical sales reports generated afterward will inaccurately reflect past state, hindering accurate trend evaluation or strategic insight extraction. Before committing to a Type 1 methodology, companies must weigh the analytical implications closely. When deeper historical analysis is a priority, Type 1 alone rarely suffices; additional methods or a hybrid approach may be beneficial.
Type 2: Historical Data Versions (Maintain History)
The Type 2 keeping history approach significantly improves analytical accuracy by preserving historical data states alongside new ones. Whenever an attribute change occurs, Type 2 stores each distinct version of a dimension as a separate, versioned row, typically marked using effective dates or flags indicating current or historical status. Widely adopted within modern organizations utilizing sophisticated tools or analytical platforms, this method supports precise, detailed audit trails and facilitates historical trend analyses that remain valid despite attribute evolution.
By leveraging Type 2, your organization maintains reliable historical reporting integrity, empowering analysts and stakeholders to glean accurate insights and trends across changing dimensions. Type 2 is ideal for compliance-oriented sectors such as healthcare or non-profit institutions deploying business intelligence, as well as organizations particular about auditability, historical record accuracy, or improved forecasting abilities.
Type 3: Adding Historical Attributes (Limited History, Easier Implementation)
An alternative to Type 2, Type 3 Slowly Changing Dimensions maintain historical context within the same record rather than storing entirely new rows. This approach typically adds additional columns specifically indicating previous states, such as “previous_region” or “alternate_position,” alongside current attribute columns. It limits historical depth but keeps scenarios simpler, making SQL queries, business logic, and analytical calculations straightforward.
Though the easiest to implement and leverage within existing database structures, Type 3 approaches come with key limitations when tracking numerous historical changes or substantial complexity. While practical for tracking infrequent and limited attribute shifts, larger-scale analytical environments with frequent or more complex evolution are advised to implement Type 2 solutions or consider composable data analytics strategies to flexibly manage complexity.
Best Practices for Implementing SCD in Modern Platforms
Modern data platforms, especially cloud-based or hybrid architecture solutions, offer unprecedented opportunities to streamline effective SCD implementation. Not every approach fits every organization’s needs; evaluating your analytical goals, data volume, complexity level, and reporting requirements is crucial. Incorporating tools that support your chosen SCD strategy seamlessly across your analytic stack—such as cloud-based data warehouses (Snowflake, BigQuery), ETL or ELT processes, or leveraging managed analytics platforms—is essential.
Additionally, consistency is critical—establish clear rules, definitions, and governance surrounding attribute change management early in the project lifecycle. Data governance frameworks, documentation standards, and clearly defined attribute catalogues before deployment drastically minimize confusion or inaccuracies downstream. Businesses should consider combining modern SCD methodologies with carefully managed data governance and visualization best practices to avoid pitfalls related to confusion or complexity. Speaking of visualization, fostering effective data visualization techniques is integral to maximizing the value derived from a well-implemented SCD schema.
Moreover, avoid unnecessary complexity or clutter in data representation—keep visualizations clean and effective to ensure insights remain digestible and action-oriented.
Embracing Innovation—Micro Applications & APIs in SCD Management
Modern data architectures aren’t restricted only to traditional databases and warehouses. Emerging innovative solutions, particularly leveraging microservices and API integrations, enhance agility and flexibility in handling Slowly Changing Dimensions. Businesses increasingly turn toward specialized, easily manageable micro-applications and agile solutions. Indeed, micro-applications represent a core trend in agile data solutions, enabling companies to incorporate changes in dimensions more efficiently and rapidly into their analytics workflows.
Similarly, leveraging robust APIs from popular industry platforms—such as Procore for construction project management—further simplifies integration and enhances reporting accuracy. Services including Procore API consulting enable businesses to efficiently synchronize dimension-related data changes throughout various business-critical applications and platforms. By incorporating modern strategies and APIs, enterprises secure a meaningful advantage in operational agility, analytical accuracy, and data governance effectiveness, ultimately ensuring their Slowly Changing Dimension approach supports continuous and actionable insights for decision-makers.
Navigating Your Path to Optimal SCD Implementation
Whether building a custom solution or leveraging off-the-shelf technology, one thing is clear—implementing Slowly Changing Dimensions strategically is crucial to modern analytics and architecture success. Understanding your organization’s analytical priorities, resources, and capabilities is fundamental. Choose strategies that align best with your business requirements, maintenance complexity, historical accuracy needs, and technical infrastructure.
As the industry evolves, continuous learning and iteration will be your closest allies. Staying informed on data architecture trends ensures your SCD strategies remain relevant. Explore valuable insights on the future of analytics through updates such as the future of data engineering trends. It’s time for your business to harness the full value offered by strategically implemented Slowly Changing Dimensions and take informed steps towards better decisions, effective governance, and stronger analytics capabilities.

by tyler garrett | May 24, 2025 | Data Visual
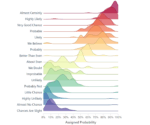
In an era where decision-making requires swift insights derived from complex data, effective visualization becomes critical. Small multiples, fundamentally an information visualization technique, deliver exceptional comparative analytical capability by breaking down intricate datasets into digestible visual segments. These small, repeated visuals arranged side by side can transform overwhelming data structures into intuitive understanding. As decision-makers and analysts grapple with the ever-increasing volume of data, small multiples offer clarity, efficiency, and precision. Today, we explore the strategic application of small multiples in comparative analysis—helping you harness data-driven insights to precision-tune your organization’s strategic vision and connect technical excellence with impactful business outcomes.
Understanding Small Multiples: What and Why?
Small multiples are simplistic yet powerful visualization techniques—utilizing repeated, uniform charts placed side by side for direct visual comparison. Rather than merging multiple data sets or cramming information into a single, unwieldy chart, each “multiple” encapsulates a singular subset of the data, facilitating swift and insightful comparison across groups. This method eliminates visual clutter and significantly increases interpretability, aiding organizational leaders and technical stakeholders alike in making informed, data-driven decisions rapidly.
In an era heavily driven by big data, visualization mechanisms can quickly become cluttered or overwhelming. Small multiples confront this challenge head-on, streamlining complex relational insights into concise, comparative grids. When compared accurately through standardized axes and scale, decision-makers leverage intuitive analytical storytelling that highlights trends and outliers clearly. Furthermore, effective comparative analysis positions your organization to proactively adjust strategies—feeding directly into advanced services such as mastering demand forecasting with predictive analytics, thus enabling optimized and efficient supply-chain operations driven by insightful visualization.
Choosing the appropriate visualization is akin to selecting the right technology stack or database platform. For teams utilizing databases like PostgreSQL, aligning the power of visualization with your database infrastructure becomes seamless through strategic alignment with trusted partners specializing in PostgreSQL consulting services.
Implementing Small Multiples Effectively in Your Organization
Selecting the Appropriate Data
A successful small multiples implementation starts with thoughtfully selecting data appropriate for comparative purposes. When embarking on comparative visualizations, prioritizing data consistency, format integrity, and clean data cleanliness are vital. Often, challenges in data quality can impede accurate interpretation, underscoring the role of robust data engineering and stable data infrastructures. Stay ahead of the curve by learning about emerging trends and how advanced data engineering trends in 2025 can boost profitability.
Furthermore, the underlying databases supplying data must support consistent and accurate comparisons. This directly influences stakeholder comprehension, ensuring accurate interpretations and, consequently, sound decision-making. Organizations should factor systematic schema practices, leveraging industry-standard schema evolution patterns with backward, forward compatibility, ensuring database agility and consistent accuracy within comparative visualizations like small multiples.
Choosing Metrics & Visual Encoding
Effective small multiples visualizations hinge on selecting meaningful metrics paired with appropriate visual encoding methods—whether color-coding, size differentiation, or shapes and forms. Technical stakeholders and decision-makers alike must prioritize clarity over complexity, employing restrained visual design choices that align visual encoding with logical data representation.
Understanding visualization foundations facilitates accuracy and meaningful synthesis; newcomers can revisit foundational principles by reviewing tutorials such as creating a basic bar chart or line graph in your preferred data visualization tool. Thoughtful selection fosters clear visual messaging enhancing both technical and strategic understanding across your organization.
Scalability and Automation of Small Multiples
Implementing automation facilitates scalable, accurate, and timely small multiples visualization solutions—a critical benefit in our speed-oriented business ecosystems. Automated visualization pipelines can depend on various workflow patterns, prompting strategic discussions around pipeline execution planning and static versus dynamic approaches. Leveraging automated frameworks ensures accurate, repeatable representations empowering decision-makers with confidence in their conclusions.
Automation aligns data governance processes effectively, safeguarding data quality, systemizing effective security, and reinforcing your analytics and reporting confidence. Integrating automation and ETL processes can enhance small multiples accuracy, as noted in various practical scenarios detailed in our blog post, 10 examples where ETL is playing a key role in data governance and security, underscoring data visualization’s integral connection to high-quality, governed datasets.
Advanced Analytics and Innovation Through Small Multiples
Leveraging Advanced Analytical Models
Organizations driving growth and profitability through innovation recognize visualization as a foundational element for advanced analytics. When visualization embraces innovative practices such as small multiples, organizations facilitate advanced analyses—including predictive analytics, trend forecasting, and comparative analyses. Small multiples combined with analytical forecasting pave the way for more sophisticated decision-making scenarios.
Executing sophisticated predictive analytics and demand forecasting requires streamlined, reliable, and robust visual communication tools. By integrating predictive analytical demand-forecasting methodologies alongside visually intuitive technologies like small multiples, enterprises significantly enhance strategic decision-making abilities—bringing tangible, actionable business outcomes to fruition.
Pushing Beyond the Boundaries
Small multiples implementation can act as a stepping stone toward revolutionary developments in technological exploration, prompting innovative strategic directions, such as exploring emerging trends and paradigm shifts. Exploring futuristic domains such as quantum computing or leveraging forward-thinking employment of Python ecosystems, like those detailed in our article on exploring four important Python libraries for enhanced development in 2023, becomes achievable with clear visualization and comparison capabilities.
By harnessing small multiples to succinctly communicate complex analytical results, organizations can focus greater resources toward innovative and visionary strategic initiatives—reinforcing their commitment to continuously advancing technological prowess.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Using Small Multiples
Effective small multiples implementation mitigates common visualization missteps such as inconsistent formats, incompatible scales, and cluttered confusion—which often lead stakeholders to ignore or gloss over your insights. For organizations experiencing low readership of impactful visualizations and reports, understanding repercussions beyond the technical implementation is essential. Our article, “No One Looks at Your Reports – Ouch”, provides valuable recommendations on addressing this critical gap, combining technical and strategic approaches effectively.
Furthermore, systematic standardization involving defined table structures and schema architecture, as discussed in our in-depth guide “Create Table: Defining a New Table Structure in SQL”, guarantees consistency across visualizations. Precise consistency leads directly to better user interpretations and enhanced comparative analysis that strengthens organizational agility, clarity, and confidence.
Conclusion: Driving Strategic Decisions Through Effective Visualization
Implementing small multiples equips organizations with the visualization power to elevate comparative analysis potential substantially. By employing thoughtfully designed, selectively automated, and strategically implemented small multiples, contemporary decision-makers transcend mere data collection—enabling insightful, actionable analytical intelligence.
Effective implementation facilitates quicker, more accurate strategic understanding, providing transformative impacts across internal and external stakeholders. Employing advanced visual analytics drives innovation and profitability. Thus, integrating small multiples into your analytics strategy confidently pushes analytical and organizational boundaries for enduring competitive advantages, allowing you to shape the organization’s technological trajectory effectively.
Thank you for your support, follow DEV3LOPCOM, LLC on LinkedIn and YouTube.

by tyler garrett | May 24, 2025 | Data Visual
In an era where data fuels strategic decision-making, delivering timely, relevant, and accessible insights to stakeholders is critical. However, relevant analytics are only as good as their accessibility—and user experience matters deeply. With business leaders, executives, and team members accessing critical information via smartphones, tablets, laptops, or large monitor walls, responsive visualization design becomes a non-negotiable imperative. As data strategists and leading-edge software consultants, we’ve seen firsthand how responsive visual design dramatically improves analytics adoption and intuitive decision-making. Building dashboards and interactive analytical visualizations isn’t merely about aesthetics or functionality in silos—it’s about creating unified, cross-device experiences that seamlessly enable insight-driven action. This is the essence of enabling genuinely responsive analytics—designing visual interfaces that tell powerful stories clearly, succinctly, and consistently, regardless of the viewing device.
Understanding the Importance of Responsive Visualization
Organizations today operate in dynamic, fast-moving environments. Executives do not have the luxury of waiting until they’re in front of a desktop monitor to make critical decisions based on analytics—nor do frontline field workers always have the convenience of secure office networks to check essential operational data. Responsive visualization design inherently acknowledges this reality by constraining and molding data-driven insights into meaningful visual outputs that fit perfectly across all types of screens and devices, ensuring accessibility and clarity anywhere.
Our experience with the tech-driven construction industry exemplifies the demand for responsive dashboards. For instance, integrating analytics with platforms through Procore API consulting services proved valuable in enabling field workers on construction sites to swiftly consume analytics through mobile interfaces. Bringing real-time data visualizations to on-the-ground teams requires dashboards optimized for smartphones or tablets, empowering rapid, well-informed decisions without reliance on desktop setups.
Incorporating responsive designs greatly supports adoption by minimizing barriers to insight consumption. As emphasized in our blog post discussing creating executive dashboards for meaningful decisions, a key success factor includes dashboards that instantly adapt to different contexts, workflows, and roles. Responsive visualizations allow executives and employees to instantly understand complex data insights, whether they’re checking a quick report on their mobile phones or analyzing performance metrics at their office desks.
Principles and Best Practices for Responsive Data Visualization
Simplicity in Data Representation
One of the fundamental principles of responsive visualization design is simplicity. Mobile devices inherently have smaller screens, requiring visual elements that communicate clearly and swiftly. Overly complex visualizations may deliver remarkable details on large desktop monitors, but quickly lose readability and usability when viewed on a smartphone device. Therefore, prioritize minimalism and simplicity to ensure the essential information is instantly recognizable and actionable.
Strategically employing visual hierarchy—highlighting critical metrics clearly, placing crucial KPIs at the forefront, and limiting excessive metrics—facilitates quick comprehension. Utilizing best practices such as progressive disclosure, straightforward bar and line charts, and a conservative color palette ensures visualizations remain impactful, ensure clarity, and offer actionable insights, even in constrained spaces.
Adaptive Content and Modular Design
Adapting for mobile devices isn’t merely about shrinking visual elements—it’s about fundamentally re-thinking content from a modular standpoint. Responsive analytics visualizations should break complex dashboards into modular tiles that can reshape flexibly, permitting enhancing content adaptability to various devices and screen orientations. Layers of interaction and data hierarchy emerge intuitively as device size and real-estate increases from smartphone to desktop.
As we’ve outlined previously in our exploration of privacy-preserving analytics with synthetic data, flexibility in viewing data at varying levels of granularity supports both comprehension and secure data handling. Responsive visualization development should similarly allow stakeholders to easily toggle between simple overviews and detailed drill-down scenarios without cognitive overload on smaller screens.
Responsive Visualization Technologies and Tools
Modern visualization tools and platforms now integrate responsiveness inherently, enabling designers and developers to create responsive dashboards efficiently. Solutions such as Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js have robust features facilitating adaptive visualizations without extensive additional coding. Beyond dashboards, building robust APIs and modern data pipelines further ensures analytical data continuously feeds responsive visualizations with accurate and up-to-date information.
Moreover, leveraging responsive visual analytics that integrate with real-time data streaming delivers significant value for rapid business decisions. As discussed in our post highlighting the importance of data streaming in fraud prevention and detection, the fusion of real-time streamed data with responsive visual interface design broadens accessibility to critical insights, eliminating latency in decision making across all devices.
Additionally, advanced monitoring solutions tailored to pipeline drift detection benefit greatly from responsive capabilities, ensuring analytics remain promptly actionable regardless of location or device. Implementing responsive visualization through innovative tooling ensures critical insights get properly presented to decision-makers wherever needed.
Overcoming Responsive Design Challenges
One inherent challenge to responsive visualization and analytics delivery is managing performance while preserving data fidelity across various devices. Smaller devices typically have less processing power, demanding optimized code and streamlined data payloads. Applying best practices like caching, intelligent data sampling, and efficient rendering significantly enhances responsive analytical performance without comprising insight accuracy.
Another critical challenge involves designing information architectures flexible enough for multiple screens while rigorous enough to convey powerful insights without confusion. As noted in our exploration of using causal inference frameworks in business decision support, structured and carefully organized information architectures contribute significantly to robust and insightful analytical experiences. Correctly applying responsive layout grids, dynamic resizing constraints, and employing iterative user testing sessions ensures analytics visuals retain meaning and efficient interaction patterns regardless of the individual end-user’s device.
We also encourage decision-makers and technical strategists adopting responsive designs to proactively learn from user feedback loops. Collaborative sessions conducted in ways similar to our post about 1-on-1 expertise sessions to improve tool adoption offer invaluable insights into user behaviors and unexpected pain points, streamlining iteration and significantly boosting visualization adoption across multiple devices.
Using Responsive Analytics to Impactful Industry-Specific Outcomes
Responsive visualization design becomes particularly impactful in addressing specific industry needs. For instance, cities currently adopting responsive analytics as part of digitally enabled sustainability strategies leverage visualization across multiple connected device categories—from public informational kiosks to smartphone reporting apps and sophisticated command centers. Our collaboration and exploration of improving Austin’s urban sustainability through analytics showcases vividly how responsive data visualization optimizes public policy implementation and community engagement significantly.
Similarly, the healthcare industry strongly benefits from responsive visualizations that accurately and clearly communicate real-time patient monitoring information and health data inputs across medical practitioners’ handheld and desktop devices. The capacity to review data fluidly from wearable devices, tablets, and desktop applications drastically improves responsiveness to medical crises or patient care adjustments.
The critical factor across these varied industries remains straightforward—increase stakeholder access and lower complexity to maximize analytics’ value proposition. Responsive visualization, when executed correctly, becomes a competitive differentiator and a facilitator for innovative analytical breakthroughs across digital transformation journeys.
Conclusion: Building Adaptable, Powerful Analytics Experiences
Responsive visualization design isn’t merely a supplementary feature to modern analytics—it’s a conversation-starting requirement. Effective analytics today demands intelligent responsiveness as stakeholders universally shift toward mobile and multi-device engagements. Organizations harnessing this responsiveness ensure deeper analytic adoption, clearer communication, improved knowledge retention, and ultimately, stronger and more informed decision-making.
At Dev3lop, our expert strategists offer not only technical expertise but also strategic roadmap support for transitioning analytics environments to wholly responsive platforms. Our commitment centers around effectively bridging the gap between data insight and real-world decision-making by enhancing data visualization accessibility, intuitiveness, and actionable outcomes across any device stakeholders leverage.
Through thoughtful, responsive analytics design, your stakeholders effectively engage and intelligently utilize data, laying the foundation for the next tier of digital innovation success.
Thank you for your support, follow DEV3LOPCOM, LLC on LinkedIn and YouTube.

by tyler garrett | May 24, 2025 | Data Visual
In today’s era of big data and analytics-driven decisions, the capacity to clearly and effectively communicate insights becomes essential. Data visualization, at its core, is not just about charts and graphs—it is about visual storytelling. Selecting an effective color palette is crucial; one incorrect color choice could make pivotal insights in your data inaccessible or misleading. While data might seem purely analytical, the science behind visualization is deeply artistic, especially when it comes to colors and their psychological implications. Implementing a proper color theory, especially color harmony, elevates data clarity, improves user understanding, and enhances decision-making accuracy. Whether you’re analyzing historical sales data, exploring multifaceted information collateral, or engaging audiences with efficient dashboards, understanding color harmony will set your visualizations apart, amplify insight communication, and drive meaningful business actions.
Understanding Color Harmony: Beyond Aesthetic Appeal
Color harmony involves a deliberate, thoughtful selection and combination of colors to create visual balance and coherence. It’s more than simply finding complementary colors; it’s understanding the psychological and cognitive impact colors have on your audience. In data visualization contexts, color harmony enhances readability and clarity, guiding the viewer naturally through data stories without unnecessary cognitive strain. Commonly used color harmony models in visual communications include analogous, monochromatic, complementary, and triadic schemes, each with distinctive impacts. Analogous colors, situated close to each other on the color wheel, create a smooth and harmonious look, ideal for categorically related data groups. Complementary schemes, involving opposite colors, enhance contrast, greatly benefiting comparative visualizations, like company performance year-over-year or the performance of regional markets. For quantitative data visualizations, monochromatic schemes utilize variations of a single color—effectively showing data intensity or magnitudes clearly without distraction.
Applying these principles requires awareness of the underlying data structure as well. Understanding your data—diversified and multifaceted by design—is key to appropriately translating data categories, hierarchical structures, or numeric scales into colors that resonate effectively. Representational clarity achieved through thoughtfully calibrated color palettes significantly reduces cognitive load, leading decision-makers toward faster, more accurate conclusions.
The Psychological and Cultural Context of Color Choices
The consideration of viewer psychology and cultural meanings behind colors is critical in data storytelling. For instance, in many Western contexts, red often signals urgency or negative values, while green embodies positivity, growth, or profitability—a distinction that proves foundational in visual representations of business’s wins and risks. However, this isn’t universally applicable, making context-awareness paramount when visualizing global data. Particularly in analyses like industry-led growth in data analytics, visualizations incorporating culturally-sensitive, clearly-defined color contexts create narratives that resonate universally and avoid misleading decision-makers.
Moreover, psychological perception factors into color palette choice. The human brain naturally associates certain colors with feelings and concepts. For example, blue hues communicate trust and stability, often appearing prominently in corporate visualizations to instill credibility. By leveraging these intrinsic psychological connotations, strategic visual design choices aid in clearly communicating complex details to stakeholders while also ensuring alignment with your company’s branding and messaging direction.
Effective visual communication, according to color harmony principles, therefore involves extensive consideration of audience perception and culturally-bound interpretations. Clear, conscious choices ensure visualizations don’t unintentionally misguide the viewer—an essential consideration when building dashboards or high-level strategic reports crucial for impactful business decisions.
Implementing Color Harmony in Data Warehousing and Visualization Projects
Bespoke data warehousing solutions and data visualizations involve vast volumes of complex data, such as those described in approaches toward data warehousing consulting services. Dealing with scalability, context-awareness, and analytics-ready architecture demands emphasis on optimized visual delivery as well. Color harmony in data visualizations within warehouses isn’t about aesthetics alone—it’s strategic biometric science. How efficiently can users discern patterns, anomalies, or opportunities via the data visualization? Color harmony matches analytic rigor with perceptual ease.
In enterprise-grade analytics solutions, data visualizations—powered by multiple internal datasets such as sales performance, production metrics, or even datasets employing temporal tables to track historical information—can be quickly made cumbersome by poor color choices. Implementing harmonious color schemes helps manage viewer attention strategically, enabling users to effortlessly identify deviations, recognize trends, and explore insights. Effective and harmonious coloration selection thus reduces visual noise and enhances user understanding, facilitating quick navigation through granular and complex scenarios—increasing usability and ensuring efficient insights.
Therefore, executing analytics-driven data initiatives should include deliberate strategizing around color-choice consistency to maintain navigability, clarity, and long-term sustainability as data volume and diversity naturally scale upward.
Pitfalls to Avoid: Common Issues When Choosing Colors for Data Visualizations
While clearly outlined benefits make color harmony increasingly attractive, it’s equally vital to understand potential pitfalls when integrating these theories into your visual outputs. Overwhelming users with excessive color variations causes visual clutter. Inappropriate color encodings for critical categorizations—for instance, representing key values with excessively similar hues—erodes interpretability. Strategic professionals recommend purposeful minimalism: limiting palettes to fewer clearly distinguishable colors, which provides visual comfort for longer explorations, as detailed in this guide on avoiding clutter and unnecessary decorations in visualizations.
Another common oversight is color vision deficiency—a critical area of accessibility in data visualization. Blues and yellows offer better color distinction for broader audiences, whereas reds and greens may hide valuable insights from affected decision-makers. Failing to verify accessibility results in partial audience alienation—countering your core visualization objectives.
Above all, avoid attaching subjective aesthetics to data sector colors without logical justifications. Every chosen hue should carry explanatory logic aligned to visualization intent, supporting your credibility and amplifying clarity. Following best practices protect dashboards from unintentionally bottlenecking decision-making clarity due to naïve or arbitrary aesthetic-driven palettes.
Innovative Approaches and Future Considerations
Innovations such as automated color palette selection leveraging environmental and context-driven insights—like those proposed in context-aware data processing frameworks—present exciting applications for future data visualization strategy. Quality analytical visuals increasingly incorporate dynamic palettes that respond swiftly to specific analytical contexts. This innovation promotes insightful storytelling, making advanced data pipelines not only context-aware but also visually responsive in real-time.
Additionally, color harmony can align seamlessly with broader initiatives like adopting content-addressable storage (CAS) for data warehousing—a storage concept explored thoroughly in this article about content-addressable storage in immutable data warehousing. Harmonious visuals amplify the effectiveness of immutable datasets, especially those retained for transparency or compliance needs.
Adaptation to evolving digital landscapes like multi-tenant cloud architectures, detailed expertly in this analysis of multi-tenant resource allocation, requires visualizations staying relevant and intuitive amidst the substantial complexities these datasets pose. Leaders and data strategists should remain adaptable about continuously exploring advancements capable of complementing sophisticated—and increasingly automated—data deployments.
Conclusion: Strategic Color Choices Drive Better Decisions
Strategic application of color harmony theory significantly elevates data visualization effectiveness. Thoughtfully applied color schemes not only enhance visual clarity but also streamline cognitive processing, enabling quicker, smarter decisions. Leveraging color harmony principles helps avoid common visualization pitfalls, incorporates psychological and cultural insights, and moves beyond aesthetics—driving actionable insights in today’s fast-paced analytics environments.
In every visualization endeavor, remember: your organization’s resource data strength mirrors not only analytical rigor but visual competence as well. Embracing strategic color harmony provides clearer vision—leading directly toward informed decision-making and tangible organizational success.
Thank you for your support, follow DEV3LOPCOM, LLC on LinkedIn and YouTube.

by tyler garrett | May 23, 2025 | Solutions
In a world constantly generating massive volumes of data, the ability to portray compelling, concise, and actionable visual information has become a fundamental skill for every modern business leader. Choosing the correct chart type isn’t merely about aesthetics—it’s about effectively communicating your message, influencing decision-making, and driving innovation. With the right data visualization strategy at your disposal, determining market trends, identifying business inefficiencies, and deriving actionable insights become significantly more intuitive and impactful. At Dev3lop, our commitment to powerful analytics and innovation-driven methodologies ensures organizations never compromise clarity for complexity. In this article, we walk you through different chart options and how to leverage each one to unlock the full potential of your data.
Understanding Good vs. Great: The Importance of Selecting Suitable Charts
When it comes to data analytics and visualization, clarity is king. Selecting the right visualization type transforms complex datasets into intuitive insights, whereas the wrong choice leads to misunderstandings, inefficiencies, and potentially misinformed business decisions. A mismatched chart leaves you “guessing” rather than knowing, turning potentially strategic assets into overwhelming heaps of ambiguity. That’s why, at Dev3lop, we advocate for clarity-driven visual analytics. Our Advanced Tableau Consulting Services emphasize creating visualizations that generate quick and tangible value.
A great visualization appeals intuitively to human perception, enabling decision-makers to identify trends and outliers instantly. Whether you’re communicating financial forecasts, mapping strategic growth, or performing predictive analytics, understanding which visualization format aligns best with your audience and intention is crucial. Experienced analysts know that inappropriate visuals might cause stakeholders to overlook critical elements or misinterpret data-driven insights entirely. On the other hand, carefully considered visualizations help professionals efficiently grasp complex information and, subsequently, make smarter operational choices—bolstering innovation, strategic foresight, and growth.
Navigating Common Chart Types and Their Uses
Bar & Column Charts: The Foundation of Clear Comparison
Perhaps the most universally understood and utilized chart type, bar and column charts are ideal for categorical comparisons and quantitative analysis. They effectively highlight the variance across multiple groups or categories, excel at illustrating rankings, and easily showcase relative magnitudes. Bar charts are your go-to visualization when you want clear comparisons at a glance.
Consider scenarios like comparing sales figures across different regions, product performance analysis, or budget allocation tracking. Bar charts simplify these visual comparisons smoothly and effectively—offering your audience an immediate understanding without information overload. To further elevate your visual analytics strategy, we recommend exploring the blend of data integration and ETL processes to unlock deeper insights. For instance, our detailed explanation on the role of ETL in data integration and data management demonstrates how data preparation sets the groundwork for impactful visuals.
Pie & Donut Charts: Perfect for Simple Proportional Relationships
Although sometimes criticized for being overly simplistic or challenging at presenting small discrepancies among slice sizes, pie and donut charts are excellent for quickly communicating straightforward topical breakdowns of data. They visualize a clear message about proportionality, especially when focusing on a limited number of categories. However, ensure these charts contain no more than five segments to maximize readability and ease of interpretation.
Useful implementations of pie charts include presentations highlighting market share, budget allocations, and small-scale stakeholder distributions. Conversely, when making precise numeric comparisons or visualizing a vast number of data points, bar charts take precedence over pie charts. Experts at Dev3lop understand data representations must always serve clarity and impact, and pie charts can indeed offer instantaneous insight—when utilized appropriately and sparingly.
Line Charts: Insights into Trends and Time Series Analysis
Line charts are invaluable when visualizing time-based data points, clarifying trends, seasonality, and fluctuations occurring over intervals. Their powerful interpretation capabilities render them essential tools for data strategists working with performance metrics or predictive analytics. From financial forecasting and resource utilization across quarters, to analytics measuring website traffic or customer engagement factors, line charts succinctly illustrate directionality and movement.
Additionally, employing line charts in conjunction with interactive tools can significantly enhance insights for executives who value real-time analysis. We cover this approach in depth in our article discussing the benefits of interactive data visualization, helping organizations realize actionable insights through more meaningful visual representations of time-series trendlines.
Specialized Charts: Taking Your Analytics to the Next Level
Scatter Plots: Identifying Correlation and Outliers
Identifying correlations between different datasets is fundamental to informed analytics. Scatter plots expertly reveal correlations, associations, and anomalies within large data sets. They prove ideal when assessing relationships between two numerical variables, such as the correlation between advertising spend and customer conversion or between monthly income and housing costs. Dev3lop leveraged such techniques effectively in our discussion on addressing Austin’s housing affordability crisis, demonstrating how recognizing significant correlations helps stakeholders make informed policy decisions.
Scatter plots also seamlessly illustrate data anomalies, enabling businesses to swiftly adjust tactics for anomaly detection, risk mitigation, or business process improvement. Knowing precisely when and how to employ scatter visualization elevates your analytics strategy into a new level of effectiveness—turning complexity into clear opportunities for innovation.
Heat Maps and Geographic Visualizations: Mapping Spatial patterns
Geographic visualizations and heat maps elevate visually intuitive representations of distribution and density, allowing businesses quick, impactful spatial insights. Whether analyzing customer distribution, tracking disease spread patterns, or pinpointing geographic market opportunities, these visuals encapsulate complexity while ensuring straightforward interpretation.
Heat maps also excel at identifying inefficiencies or potential opportunities in large-scale datasets. For instance, mapping traffic data, website interaction, or sales concentration reveals strategic opportunities. To achieve maximum benefit, combine geographic charts efficiently with data pipelines; we recommend assessing robust pipeline strategies such as those described in our article comparing Tableau Prep vs Python for data pipelines. This cross-functionality ensures your spatial visualizations are as timely and powerful as possible.
Techniques for Advanced Data Visualization & Analytics
When visualizing more complex, multidimensional data, adopting sophisticated visualization and analytics techniques becomes essential. Data-driven innovation involves following best practices, like ensuring data consistency, preparing data efficiently with trusted tools and processes, and using streamlined data ingestion and querying. Insights into selecting database technologies to store large-scale information, such as we explore deeply in examining PostgreSQL vs SQL Server, provide foundational support for advanced visual interpretation.
Moreover, harnessing efficient querying strategies remains key for accurate and agile analytics; the streamlined methodology outlined in our guide on the SQL IN operator for efficient filtering further highlights this. Properly paired data engineering approaches, optimized querying, and sound visualization selection enable businesses greater agility, speed, and depth in analytics.
Finally, integrating automation and advanced scheduling strategies, as Dev3lop does through the launch of our Canopys Task Scheduler software, streamlines operations and facilitates real-time visual analytics and reporting. Together, these practices amplify your advanced analytics capabilities, empowering strategic and innovative decision-making.
Conclusion: Choosing Wisely, Executing Strategically
Choosing the perfect chart to visualize your data means knowing your audience, understanding the insights to communicate, and leaning into strategic technological choices to achieve optimal visual clarity. At Dev3lop, we appreciate that your data visualization and analytics strategy requires precise intentionality and specialization.
By carefully aligning each chart type with its intended purpose, embracing advanced visualization practices, and making strategic decisions backed by robust data engineering and analytics insights, your organization moves confidently from simple data presentation to strategic analytics-driven innovation. Know your purpose, select wisely, and allow world-class visual analytics to accelerate your organization’s readiness for informed action, industry leadership, and breakthrough innovations.