The Unique Filter Node or Unique Tool finds unique values per row in your data pipelines, or allows people to quickly review duplicates only.
Plus, you can select what column(s) to find unique values within. This enables people to easily understand what is inside of a column.
Duplicate rows happen, The Unique Filter node manages these rows for you automatically.
Whether you’re eager to only look at unique rows or drilling into the duplicates, ET1’s Unique Filter Node is the data engineering tool for your unique or duplicated needs.
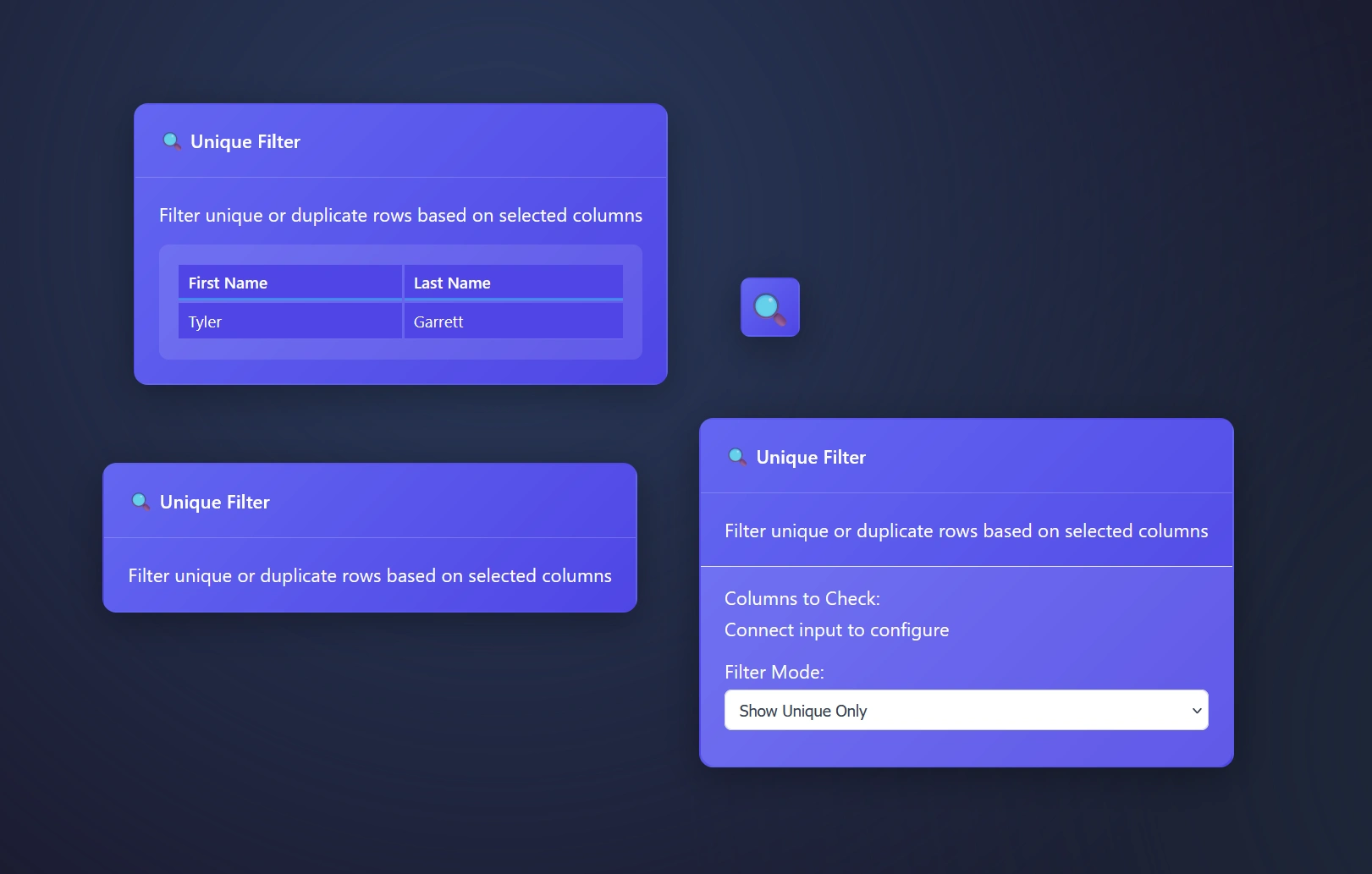
Unique Filter Node: Filter mode explained
The Unique Tool or Unique Filter Node
- Show unique only – this setting means you will stream only the unique values through the pipeline
- You may want to run this across all pipelines as a way to verify
- This is an easy way to create look up tables
- Build a tool to understand what is inside of a column
- Show duplicate only – will stream duplicates only and remove the unique values found
- Drill into duplicates only, great for deep dives and researchers
- Helpful for auditing pipelines, does your pipeline have duplicates?
Using the Unique Filter Node in ET1
Drag and drop your data pipeline arrow connection to the input of the Unique Filter to begin immediately reporting on unique rows only.
Open the settings for more granular options.
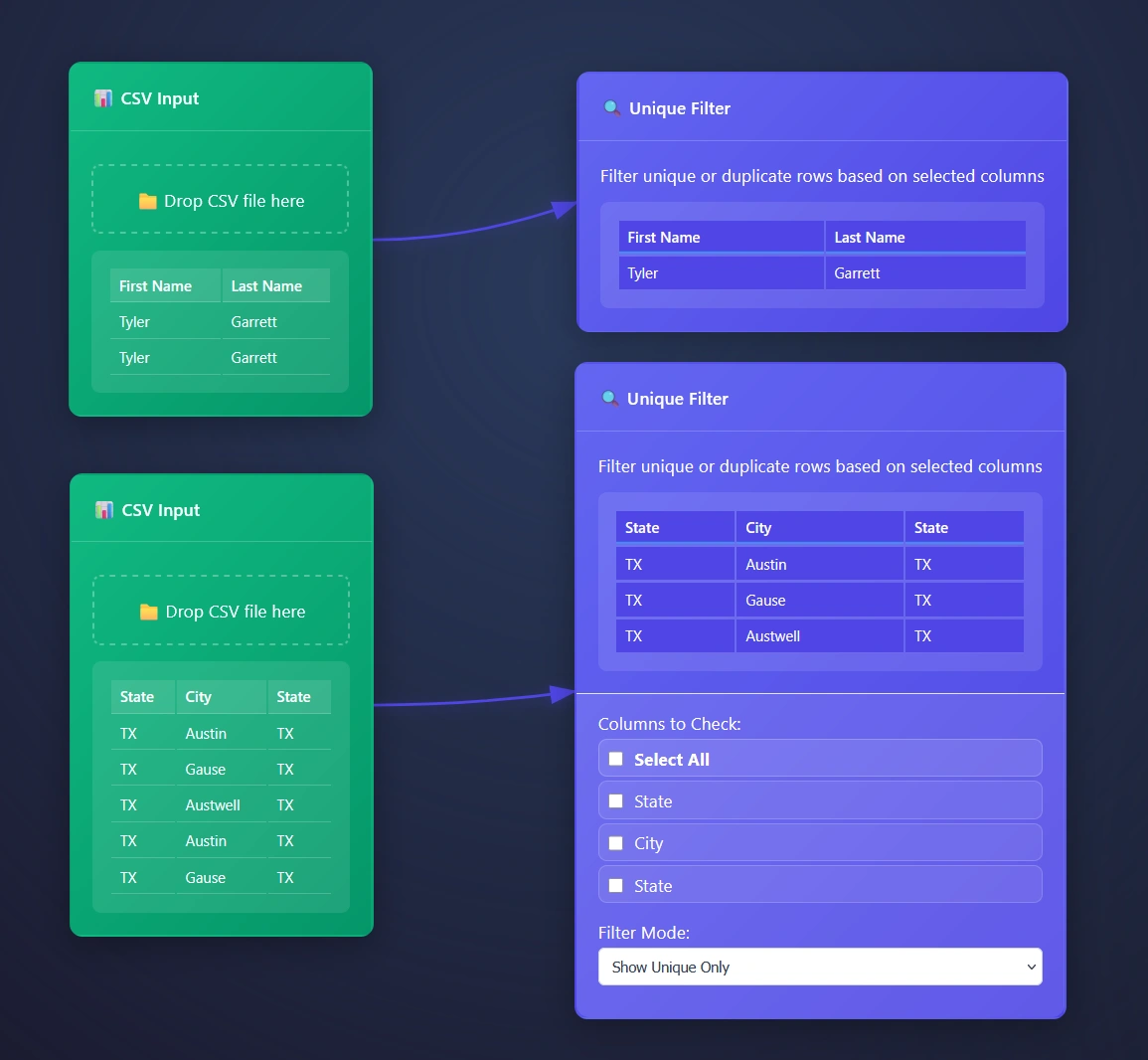
ET1’s Unique Filter Node automatically removes duplicate rows based on selected columns, however we automatically infer you are eager to use all columns and start there. Opening the settings for more options will offer a cool way to group data.
Creating look up tables with Unique Filter Node
Auditing your column? How about the values inside of each column? This is a great tool for understanding what is possible in your data pipeline.
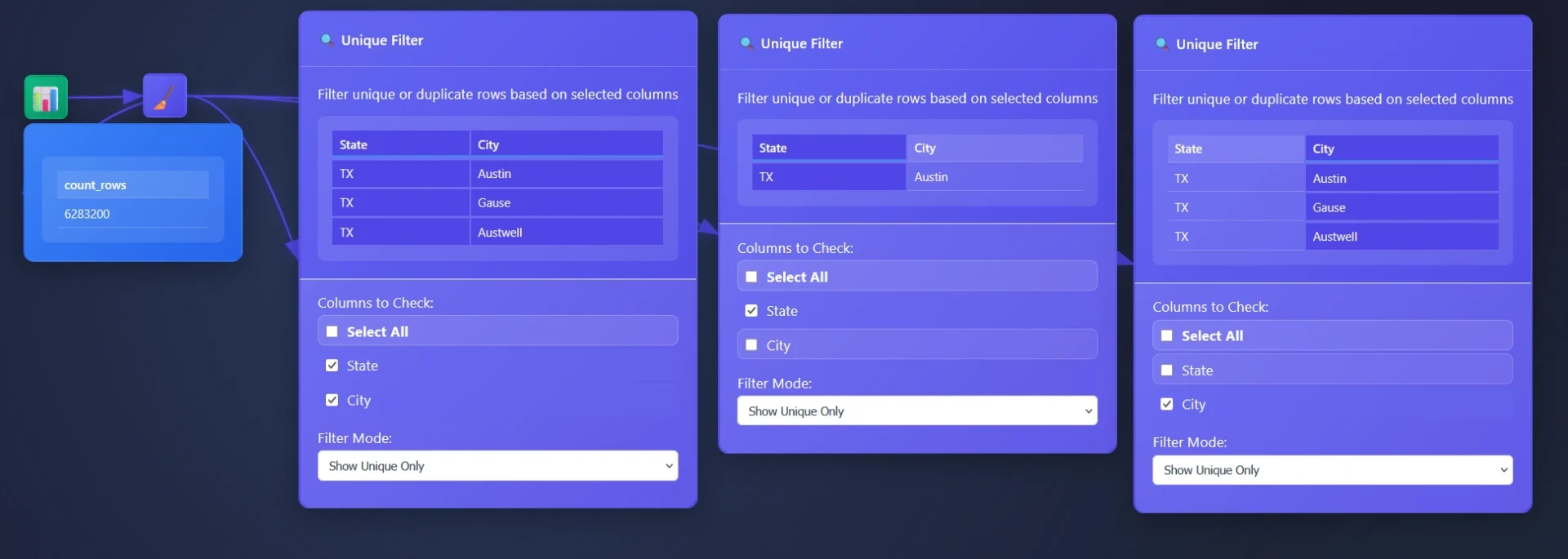
In this example, a dataset comprising 6 million transactions is provided through an email you never wish you looked at, and the objective is to identify the originating cities. While an aggregation tool could be utilized (where you are able to use group by) the Unique Tool offers another approach.
The Unique Tool facilitates a comprehensive understanding of individual column content. A common strategy involves removing unnecessary columns and employing the Unique Filter Node to extract the distinct values within the remaining table, thereby enabling the surfacing of valuable insights.
ET1 is designed to facilitate straightforward data filtering and transformation processes. It is helpful to consider data analysis as a communicative exchange with the dataset.
Technical specs on the Unique Tool’s Data Processing
JavaScript that filters data rows for uniqueness or duplication based on specified columns.
It processes tabular data in a browser-based ETL pipeline, determining which rows are unique or duplicate by constructing composite keys from selected column values. The behavior depends on the filterMode configuration: when set to 'unique', it retains only the first occurrence of each key; when set to 'duplicates', it excludes first occurrences and keeps only subsequent repeats.
- Composite keys use a rare delimiter (
'␟'): The characterU+241F(Symbol for Unit Separator) is used to join column values into a single key string. This prevents collisions that could occur with common delimiters like commas or pipes, especially when column values themselves contain such characters. - Robust handling of missing or invalid configurations: If
node.columnsis not an array or contains invalid column names, the function defaults to using all available headers, ensuring that filtering still occurs meaningfully instead of failing silently or throwing errors. - Two-pass algorithm ensures correctness: The first pass counts all key occurrences, which could be used for analytics (though currently unused); the second pass performs the actual filtering. This structure allows future enhancements, such as filtering by occurrence count thresholds.
Return to ET1 Overview to learn more.